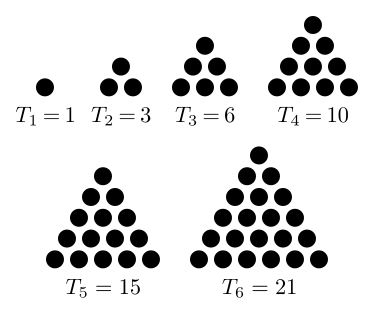
A triangular number is one that counts the number of objects in an equilateral triangle, as above:
1
1 + 2 = 3
1 + 2 + 3 = 6
1 + 2 + 3 + 4 = 10
1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5 = 15
1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5 + 6 = 21
Some of these numbers are palindromes, numbers that read the same backward and forward. A few examples are 55, 66, 171, 595, and 666. In 1973, Charles Trigg found that of the triangular numbers less than 151340, 27 are palindromes.
But interestingly, every string of 1s:
1
11
111
1111
11111
…
… is a palindromic triangular number in base nine. For example:
119 = 9 + 1 = 10
1119 = 92 + 9 + 1 = 91
11119 = 93 + 92 + 9 + 1 = 820
111119 = 94 + 93 + 92 + 9 + 1 = 7381
The pattern continues — all these numbers are triangular.
02/12/2017 UPDATE: Reader Jacob Bandes-Storch sent a visual proof:
“Given a number n in base 9, if we tack a 1 on the right, the resulting number is 9*n + 1. (By shifting over one place to the left, each digit becomes nine times its original value, and then we add 1 in the ones place.) So given a triangular number, there’s probably a way of sticking together 9 copies of it with a single additional unit to form a new triangle. Sure enough:”