
“He who falls in love meets a worse fate than he who leaps from a rock.” — Plautus
(The painting is by Edmund Leighton, 1852–1922. He called it simply Off.)

“He who falls in love meets a worse fate than he who leaps from a rock.” — Plautus
(The painting is by Edmund Leighton, 1852–1922. He called it simply Off.)
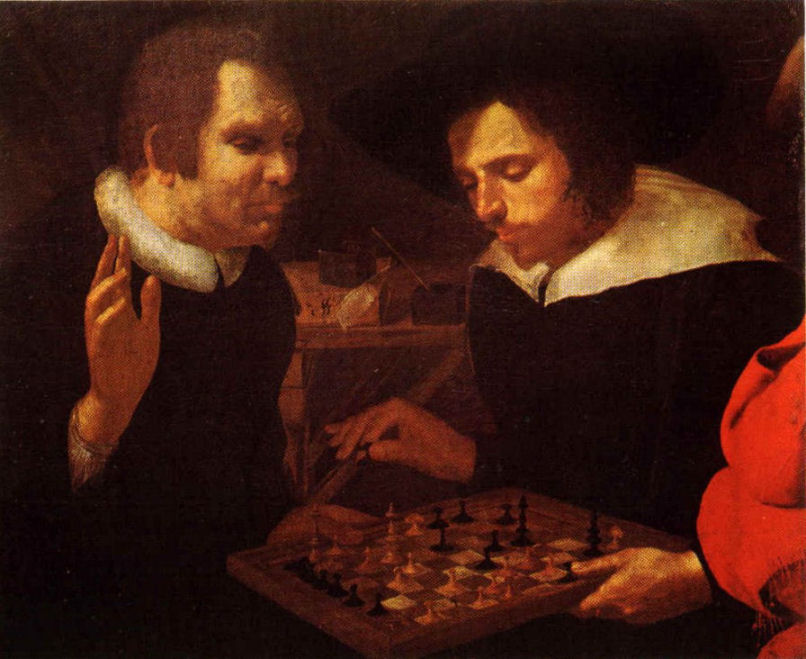

The title of this painting is electrifying: Ben Jonson and William Shakespeare Playing at Chess. Unfortunately, its authenticity has been subject to debate for more than a century. It came to light only in 1878, when it was purchased for $18,000 by Colonel Ezra Miller, and the authenticating documents were lost in a fire 17 years later.
Supporters claim that it was painted by Karel van Mander (1548-1606), and in the best possible case it would give us new likenesses of Jonson and Shakespeare painted by a contemporary. But a biography of van Mander, probably written by his brother, makes no mention of this painting, nor of the artist ever visiting London, and while Shakespeare here appears younger than Jonson, in fact he was eight or nine years older.
“It is understandable that there is still curiosity about Shakespeare’s life, physical features, and reputation,” wrote Roehampton Institute scholars Bryan Loughrey and Neil Taylor in 1983. “If the chess portrait were genuinely a portrait of Shakespeare and Jonson, the painting would be of unique interest. Unfortunately, most of the arguments that have been advanced in its favor are untenable.”
Real or fake, Shakespeare has the better of Jonson in this game — he can mate on the move:
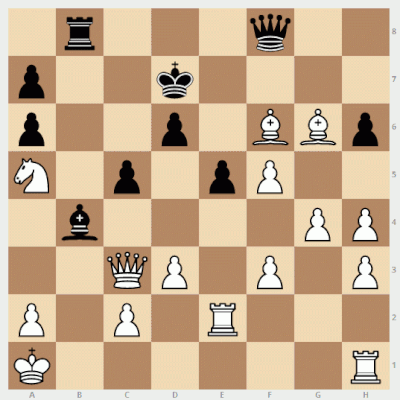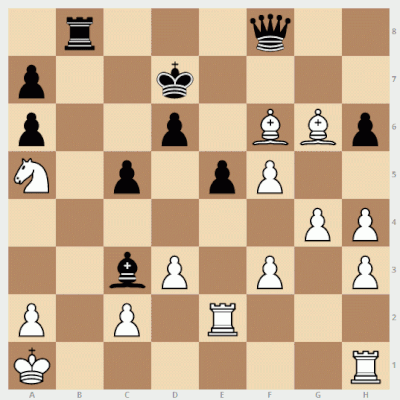
(Bryan Loughrey and Neil Taylor, “Jonson and Shakespeare at Chess?” Shakespeare Quarterly 34:4 [Winter 1983], 440-448.)
The media pavilion for the 2002 Swiss National Expo was a cloud. Organizers built a curved building fitted with more than 30,000 nozzles that pumped water from Lake Neuchâtel into a fine mist, creating a floating 90-meter fog bank whose contours were controlled by a computerized weather system.
Artist Antony Gormley took this idea a step further in 2007 with Blind Light, a 10-meter-square glass vitrine filled with mist and lit by 7,000 lux of intense fluorescent light that reduced visibility to less than an arm’s length.
“One could, and did, get temporarily lost in its 90 percent humidity,” writes Richard Hamblyn in Clouds: Nature and Culture (2017). “The intended effect of Gormley’s ‘bright, cuboid cloud’ was to overwhelm the senses, as though one had walked into a cloud, literally and figuratively, entering a cold, damp, unsettling world of enveloping isolation.”
“The hardest of all adventures to speak of is music, because music has no meaning to speak of. If music could be translated into human speech it would no longer need to exist. Like love, music’s a mystery which, when solved, evaporates.” — Ned Rorem, Music From Inside Out, 1967
“Music has no subject beyond the combinations of notes we hear, for music speaks not only by means of sounds, it speaks nothing but sound.” — Eduard Hanslick
“Music expresses that which cannot be said and on which it is impossible to be silent.” — Victor Hugo
But music moves us, and we know not why;
We feel the tears, but cannot trace their source.
Is it the language of some other state,
Born of its memory? For what can wake
The soul’s strong instinct of another world,
Like music?
— Letitia Elizabeth Landon, The Golden Violet, 1827
Sculptor Edward Ihnatowicz’s Sound Activated Mobile (SAM) was the first moving sculpture that could respond actively to its surroundings. Listening through four microphones in its head, it would twist and crane its neck to face the source of the loudest noise, like an earnest poppy.
Fascinated Londoners spent hours vying for SAM’s attention at the 1968 Cybernetic Serendipity exhibition. Encouraged, Ihnatowicz unveiled the prodigious Senster two years later.
Guillaume de Machaut’s Rondeau 14, from the 14th century, is a crab canon over a palindrome: When the singers reach the end of the line, the tenor (the lowest voice) reverses course and reads his music backward, and the other two voices follow suit, exchanging parts.
So they arrive where they started. De Machaut titled the piece “Ma fin est mon commencement” — “In my end is my beginning.”
In planning the lighting and atmosphere for Skull Island in 1933’s King Kong, animator Willis O’Brien relied heavily on Gustave Doré. In 1930 special effects expert Lewis W. Physioc had said, “If there is one man’s work that can be taken as the cinematographer’s text, it is that of Doré. His stories are told in our own language of ‘black and white,’ are highly imaginative and dramatic, and should stimulate anybody’s ideas.”
“The Doré influence is strikingly evident in the island scenes,” write Orville Goldner and George E. Turner in The Making of King Kong (1976) (click to enlarge). “Aside from the lighting effects, other elements of Dore illustrations are easily discernible. The affinity of the jungle clearings to those in Dore’s ‘The First Approach of the Serpent’ from Milton’s ‘Paradise Lost’ [left], ‘Dante in the Gloomy Wood’ from Dante’s ‘The Divine Comedy,’ ‘Approach to the Enchanted Palace’ from Perrault’s ‘Fairy Tales’ [right] and ‘Manz’ from Chateaubriand’s ‘Atala’ is readily apparent. The gorge and its log bridge bear more than a slight similarity to ‘The Two Goats’ from ‘The Fables’ of La Fontaine, while the lower region of the gorge may well have been designed after the pit in the Biblical illustration of ‘Daniel in the Lion’s Den.’ The wonderful scene in which Kong surveys his domain from the ‘balcony’ of his mountaintop home high above the claustrophobic jungles is suggestive of two superb Doré engravings, ‘Satan Overlooking Paradise’ from ‘Paradise Lost’ and ‘The Hermit on the Mountain’ from ‘Atala.'”
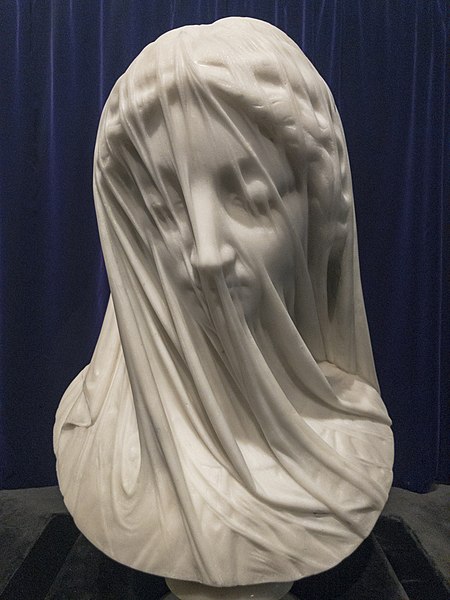

Sculptor Giovanni Strazza probably completed this bust of a veiled Virgin Mary in the early 1850s. It was transported to Newfoundland and placed in the Episcopal Palace next to St. John’s Basilica.
“To say that this representation surpasses in perfection of art, any piece of sculpture we have ever seen, conveys but weakly our impression of its exquisite beauty,” wrote a local newspaper. “The possibility of such a triumph of the chisel had not before entered into our conception. Ordinary language must ever fail to do justice to a subject like this — to the rare artistic skill, and to the emotions it produces in the beholder.”
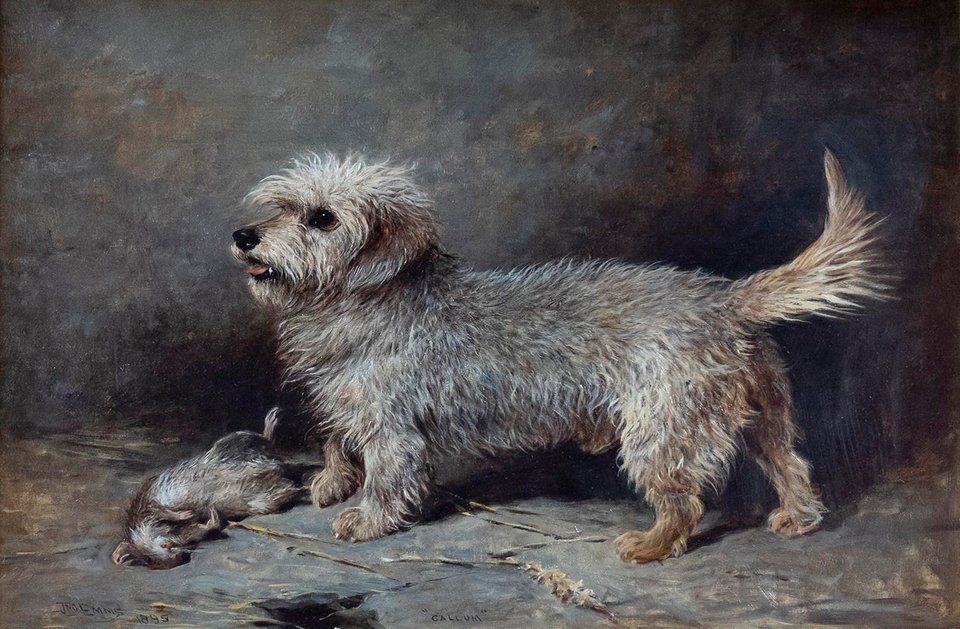

In 1919, engineer James Cowan Smith bequeathed £55,000 to the National Gallery of Scotland.
He set two conditions. One was that the gallery provide for his dog Fury.
The other was that this picture of his previous dog Callum, by painter John Emms, always be hung in the gallery.
Both conditions were fulfilled.
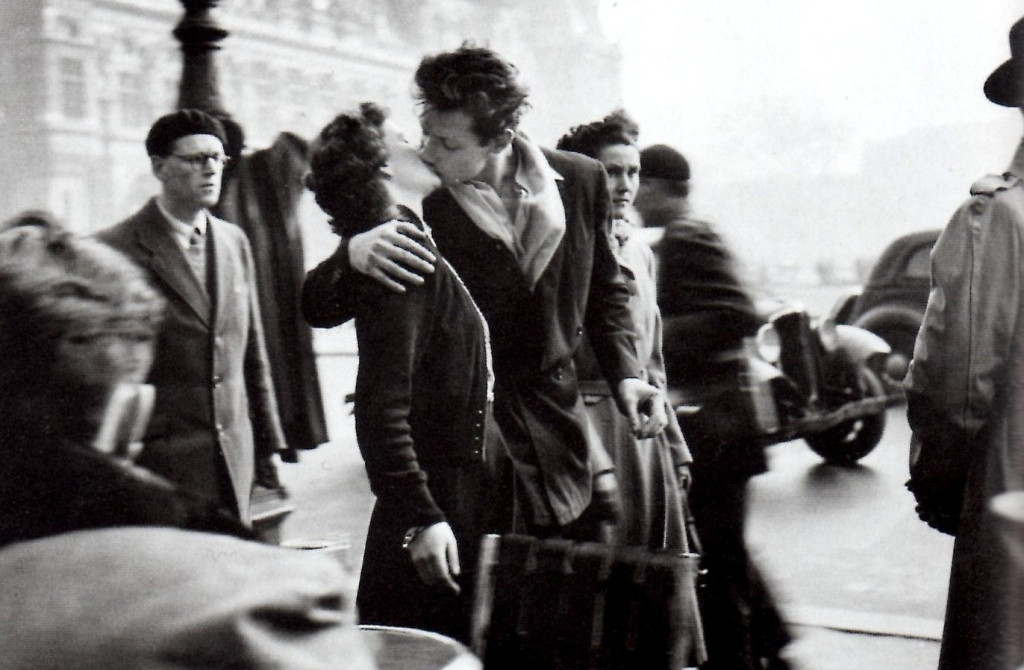

Robert Doisneau’s iconic photograph of young love in Paris sold thousands of posters, but the identity of the couple remained a mystery for decades. In 1988 Jean-Louis and Denise Lavergne saw it on a magazine cover and thought they recognized themselves: They’d been on the rue de Rivoli on April 1, 1950, and had a diary to prove it, and Lavergne still had the skirt and jacket she’d worn that day. They contacted Doisneau, who greeted them warmly but did not offer to share any of the five-figure income he’d been making each year from the poster.
When they sued him, he revealed that he’d posed the shot using Françoise Delbart and Jacques Carteaud, a couple he’d seen kissing in the street but had not dared at first to photograph. Finally he’d approached them and asked them to repeat the kiss. Delbart said, “He told us we were charming, and asked if we could kiss again for the camera. We didn’t mind. We were used to kissing.”
A thousand bubbles burst, the Lavergnes lost their suit, and Delbart eventually sold the print Doisneau had given her to feign a spontaneous kiss. She didn’t share the proceeds with Carteaud — they’d broken up nine months after the photo was taken.