
“One of the strangest things about life is that the poor, who need the money most, are the very ones that never have it.” — Finley Peter Dunne

“One of the strangest things about life is that the poor, who need the money most, are the very ones that never have it.” — Finley Peter Dunne
By Wikimedia user Cmglee, a visual proof that 33 + 43 + 53 = 63:
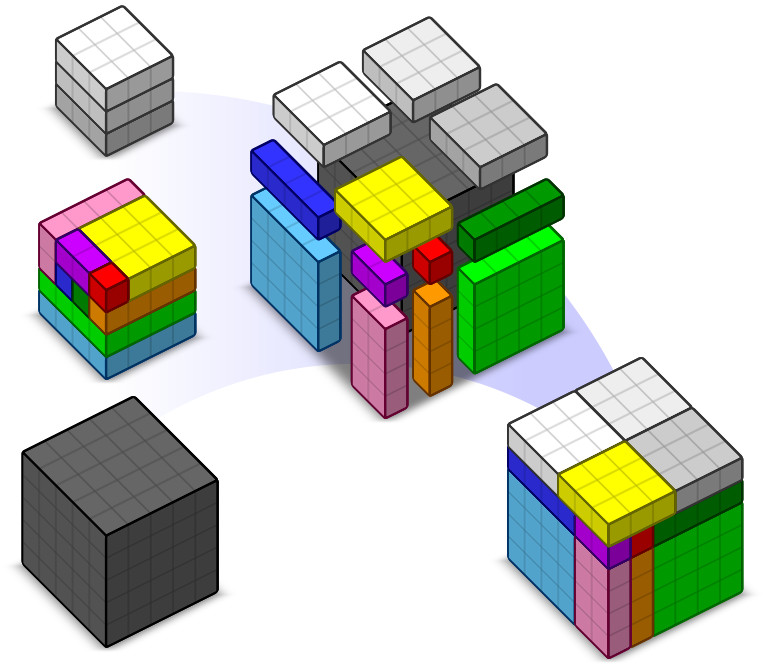
This value, 216, is sometimes called Plato’s number because it seems to correspond to this enigmatic passage in the Republic:
Now for divine begettings there is a period comprehended by a perfect number, and for mortal by the first in which augmentations dominating and dominated when they have attained to three distances and four limits of the assimilating and the dissimilating, the waxing and the waning, render all things conversable and commensurable with one another, whereof a basal four-thirds wedded to the pempad yields two harmonies at the third augmentation, the one the product of equal factors taken one hundred times, the other of equal length one way but oblong,-one dimension of a hundred numbers determined by the rational diameters of the pempad lacking one in each case, or of the irrational lacking two; the other dimension of a hundred cubes of the triad. And this entire geometrical number is determinative of this thing, of better and inferior births.
Unfortunately, Plato’s meaning is far from certain. Other values that have been proposed (with various rationales) include 1,728, 3,600, 5,040, 8,128, 17,500, 760,000, and 12,960,000. Cicero politely described the question as “obscure”; it remains open.
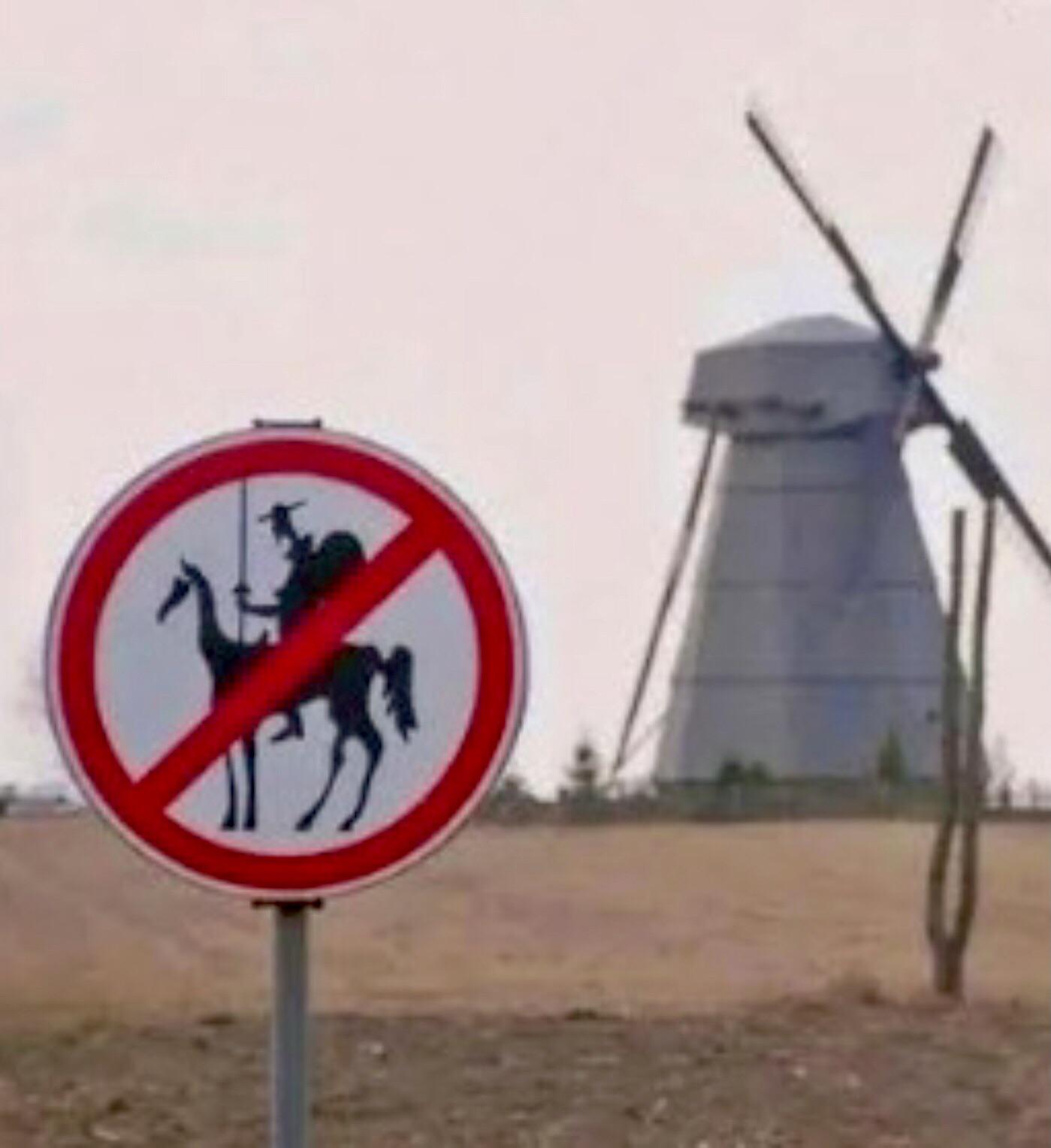

I don’t know anything about this; it just popped up on the subreddit r/funny:
“Someone in the Netherlands has a sense of humor.”
06/02/2025 UPDATE: Oop, no, it’s at the Dudutki ethnographic museum in Minsk! (Thanks, Nick.)

In the December 2024 issue of Recreational Mathematics Magazine, Illinois State University mathematician Sunil Chebolu demonstrates that the digits of π can be generated using the positions of stars.
The probability P(x, y) that two randomly chosen positive integers, x and y, are relatively prime is 6/π2. The stars in the night sky appear to be distributed randomly on the celestial sphere, and this suggests a novel experiment: Use the pairwise angular distances between stars to simulate a large random sample of numbers, then pick random pairs and determine the proportion of relatively prime pairs. Equating that with the theoretical probability above should generate an approximation of π.
In Nature in 1995, University of Aston mathematician Robert Matthews used the positions of 100 stars to compute π to within 0.5% of its correct value (3.12772). By expanding the sample to 1,000 stars, Chebolu got an average estimate of 3.141540567, an error of less than 0.002%.
“The above method can also be viewed as a statistical hypothesis test,” Chebolu notes. “Since the error in the estimate for π obtained using this method is pretty low, one may also argue that it supports the hypothesis that the bright stars are randomly distributed on the celestial sphere.”
(Sunil K. Chebolu, “Baking Star π,” Recreational Mathematics Magazine 11:19 [December 2024], 67-70.)
postation
n. the placing of one thing after another
consectaneous
adj. succeeding, following as by consequence
resiliating
adj. that resumes or causes to resume a former shape or position
finifugal
adj. shunning the end of something
Jason Allemann built this infinite LEGO domino ring in 2023. Sixty-four dominoes fall in a continuous loop, with a robot circulating perpetually opposite the cascade to restore the tiles to their standing state.
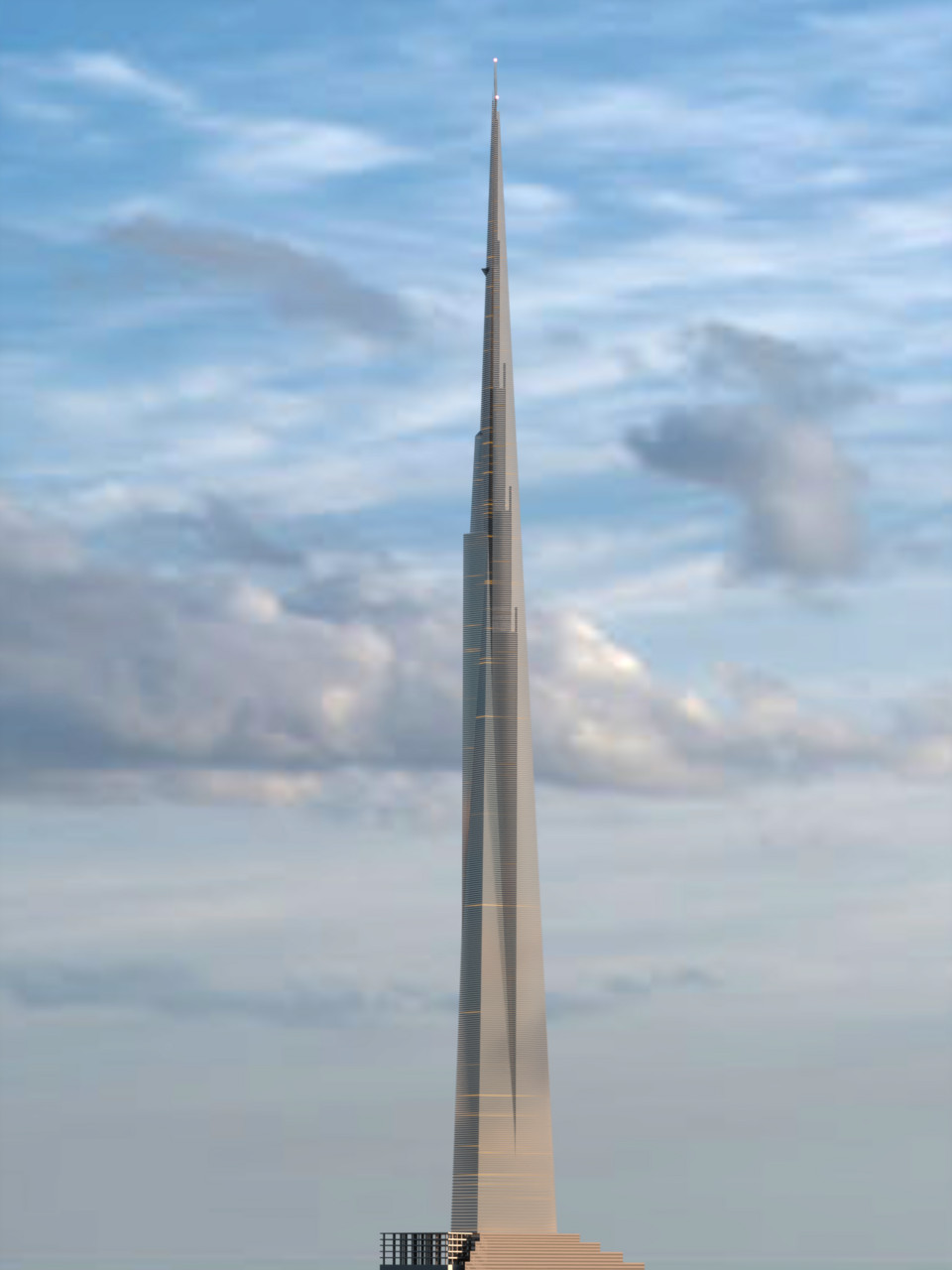

In his 1957 book A Testament, Frank Lloyd Wright described a skyscraper a mile high that he hoped to build in Chicago. Atomic-powered elevators would serve a net rentable area of more than 13 million square feet, with covered parking for 15,000 cars and landing decks for 150 helicopters.
Wright imaged it would be “more permanent than the pyramids,” but the plan was never realized. The 528-story building would have been nearly twice as tall as the Burj Khalifa and four times the height of the Empire State Building.

In discussing the paintings, [Jackson Pollock] would ask, ‘Does it work?’ Or in looking at mine, he would comment, ‘It works’ or ‘It doesn’t work.’ He may have been the first artist to have used the word ‘work’ in that sense.
— Lee Krasner, quoted in B.H. Friedman, Jackson Pollock: Energy Made Visible, 1972

In 1937 a Sabena Junkers Ju 52 crashed in Ostend — the plane struck a factory chimney while attempting to land in thick fog. Everyone aboard was killed, including Princess Cecilie, the older sister of Prince Philip, later Duke of Edinburgh.
She had been eight months pregnant, and a newborn infant was discovered in the wreckage. It’s speculated that she had given birth during the flight, and that this had led the pilot to try to land in hazardous conditions.
In his later years Joseph Conrad became obsessed with the opening scene of an unwritten novel that he planned to set in an Eastern European state. “So vividly used he to describe this scene to me,” wrote his friend Richard Curle, “that at last it was as though I had been a witness to it myself”:
“In the courtyard of a royal palace, brilliantly lighted up as for a festival, soldiers are bivouacked in the snow. And inside the palace a fateful council is taking place and the destiny of the country is being decided.”
“I never learned anything more about this novel — I do not know how far Conrad had himself visualized the plot,” Curle wrote, “but as he pictured that opening scene one could almost feel the tension in the air and one almost seemed to be warming one’s hands with the soldiers around their blazing fire.”
(Richard Curle, The Last Twelve Years of Joseph Conrad, 1928.)
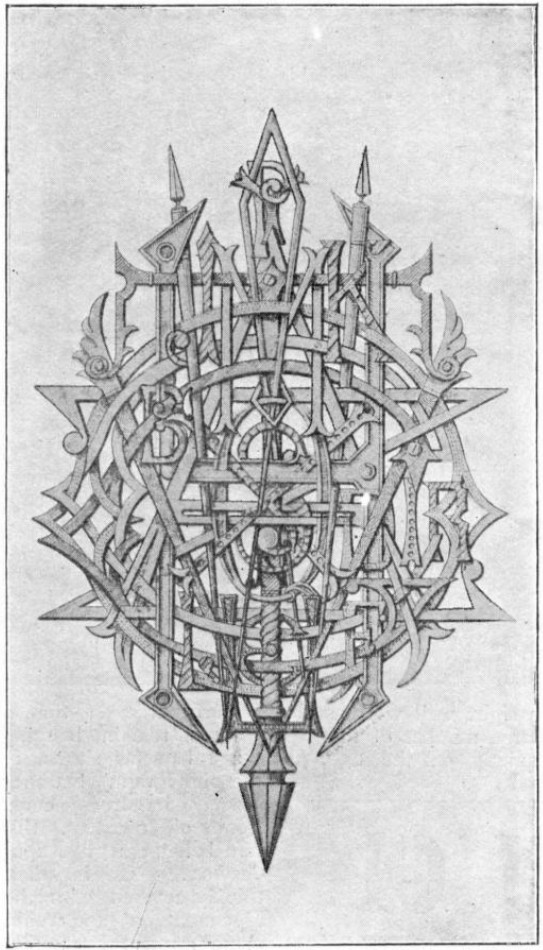
C.W. Hooper of Keswick sent this creation to the Strand in August 1901: “It contains all the letters of the alphabet, twenty-six in all. They can be traced with patience. The letter N is the smallest (in the centre), and is the only indistinct one.”