quisquous
adj. difficult to deal with or settle
quillet
n. a verbal nicety, a subtle distinction
aggiornamento
n. the act of bringing something up to date to meet current needs
irenic
adj. fitted or designed to promote peace
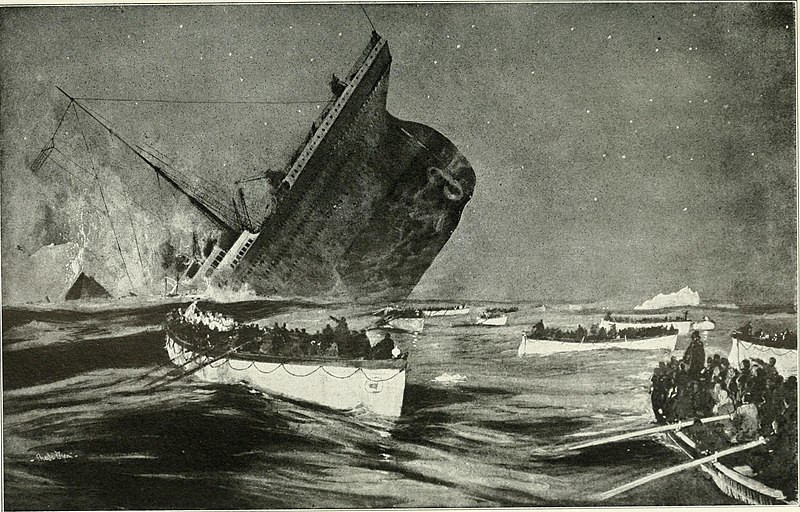
The survivors of the Titanic were picked up by the English passenger steamship Carpathia, which conveyed them to New York. This presented a delicate problem to the Social Register. “In those days the ship that people travelled on was an important yardstick in measuring their standing, and the Register dutifully kept track,” notes Walter Lord in A Night to Remember (1955). “To say that listed families crossed on the Titanic gave them their social due, but it wasn’t true. To say they arrived on the plodding Carpathia was true, but socially misleading. How to handle this dilemma? In the case of those lost, the Register dodged the problem — after their names it simply noted the words, ‘died at sea, 15 April 1912’. In the case of those living, the Register carefully ran the phrase, ‘Arrived Titan-Carpath, 18 April 1912’. The hyphen represented history’s greatest sea disaster.”



