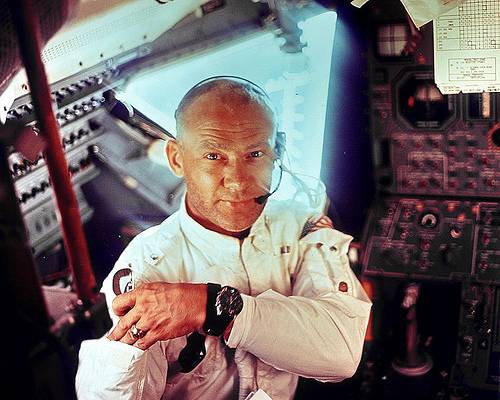
Buzz Aldrin celebrated communion on the moon. From his 2009 book Magnificent Desolation:
So, during those first hours on the moon, before the planned eating and rest periods, I reached into my personal preference kit and pulled out the communion elements along with a three-by-five card on which I had written the words of Jesus: ‘I am the vine, you are the branches. Whoever remains in me, and I in him, will bear much fruit; for you can do nothing without me.’ I poured a thimbleful of wine from a sealed plastic container into a small chalice, and waited for the wine to settle down as it swirled in the one-sixth Earth gravity of the moon. My comments to the world were inclusive: ‘I would like to request a few moments of silence … and to invite each person listening in, wherever and whomever they may be, to pause for a moment and contemplate the events of the past few hours, and to give thanks in his or her own way.’ I silently read the Bible passage as I partook of the wafer and the wine, and offered a private prayer for the task at hand and the opportunity I had been given.
“Perhaps, if I had it to do over again, I would not choose to celebrate communion,” he wrote. “Although it was a deeply meaningful experience for me, it was a Christian sacrament, and we had come to the moon in the name of all mankind — be they Christians, Jews, Muslims, animists, agnostics, or atheists. But at the time I could think of no better way to acknowledge the enormity of the Apollo 11 experience that by giving thanks to God.”