
Man: Hello, my boy. And what is your dog’s name?
Boy: I don’t know. We call him Rover.
— Stafford Beer

Man: Hello, my boy. And what is your dog’s name?
Boy: I don’t know. We call him Rover.
— Stafford Beer
A writer in The Builder has cleverly suggested that bridges might be erected in the crowded thoroughfares of London for the convenience of foot passengers, who lose so much valuable time in crossing. As the stairs would occupy a considerable space, and occasion much fatigue, I beg to propose an amendment: Might not the ascending pedestrians be raised up by the descending? The bridge would then resemble the letter H, and occupy but little room. Three or four at a time, stepping into an iron framework, would be gently elevated, walk across, and perform by their weight the same friendly office for others rising on the opposite side. Surely no obstacles can arise which might not be surmounted by ingenuity. If a temporary bridge were erected in one of the parks the experiment might be tried at little cost, and, at any rate, some amusement would be afforded. C.T.
— Notes and Queries, July 17, 1852
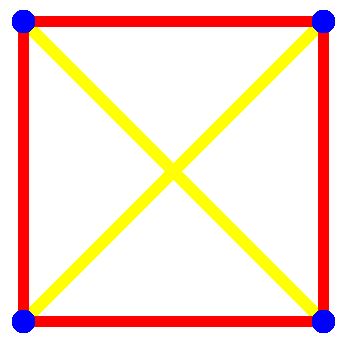
Alex Bellos set a pleasingly simple puzzle in Monday’s Guardian: How many ways are there to arrange four points in the plane so that only two distances occur between any two points? He gives one solution, which helps to illustrate the problem: In a square, any two vertices are separated by either the length of a side or the length of a diagonal — no matter which two points are chosen, the distance between them will be one of two values. Besides the square, how many other configurations have this property?
The puzzle comes originally from Dartmouth mathematician Peter Winkler, who writes, “Nearly everyone misses at least one [solution], and for each possible solution, it’s been missed by at least one person.”
In On the Origin of Species, Darwin wrote that bumblebees are the only pollinators of red clover.
In 1862 he discovered that this is wrong — honeybees do it as well.
He wrote to his friend John Lubbock, “I hate myself, I hate clover, and I hate bees.”
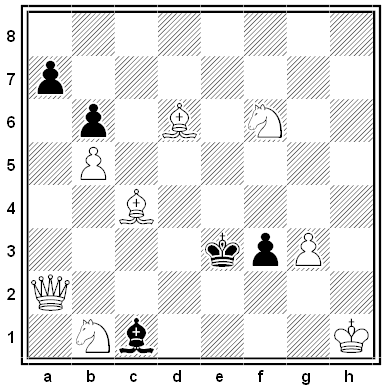
“A fairly good two-mover” from Benjamin Glover Laws’ The Two-Move Chess Problem, 1890. What’s the key move?
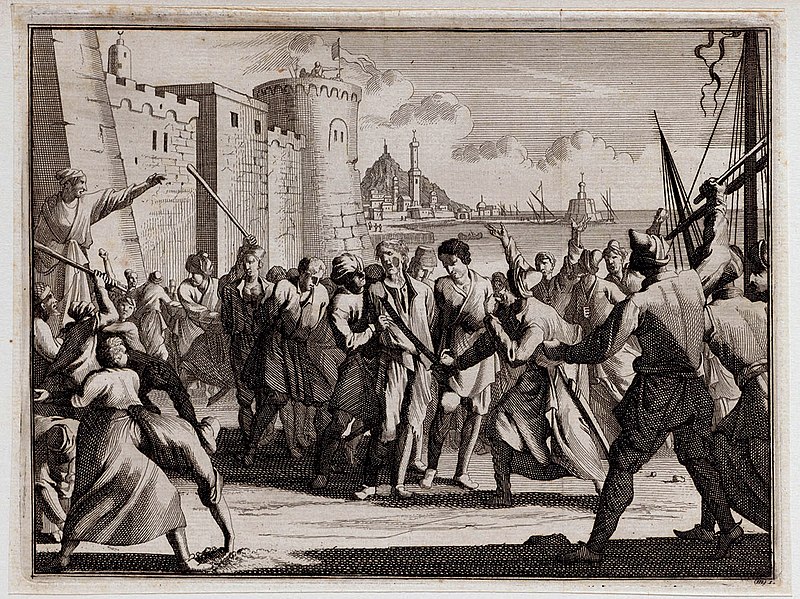

One night in 1631, pirates from the Barbary coast stole ashore at the little Irish village of Baltimore and abducted 107 people to a life of slavery in Algiers — a rare instance of African raiders seizing white slaves from the British Isles. In this week’s episode of the Futility Closet podcast we’ll describe the sack of Baltimore and the new life that awaited the captives in North Africa.
We’ll also save the Tower of London and puzzle over a controversial number.

Revenue agents in 18th-century London faced a curious challenge: how to calculate the excise tax on a barrel that was partially full of liquor. The answer was an “ullage slide rule” — this gauging rod was dipped into the barrel, some brass sliding pieces were adjusted to reflect the height of the surface, and a mathematical calculation would tell how much liquid the barrel contained.
The Science Museum says, “The calculations were very complicated.” A correspondent to the Mathematical Gazette wrote in 1990, “I well remember puzzling, unsuccessfully, over graphs and calculations of measurements until I wrote to the makers whose name was stamped on the rule and who still existed [in 1966] at the same address in London Bridge. At that time they were still making a modern equivalent for the same use by revenue officers.” More at the link below.
(Tom Martin, “Gauging: The Art Behind the Slide Rule,” Brewery History 133 [2009], 69-86.)

Ishmael narrates Moby-Dick, just as Gulliver narrates his travels and John Watson narrates the Sherlock Holmes stories. In each case we can assume that all the information presented in the literary story is imparted to us by its fictional narrator.
But the filmed version of each story contains thousands of details that are apparent to us but clearly never observed directly by the narrator. Yet it’s still the narrator who’s ostensibly telling us the story. If the narrator isn’t supplying these details, then … who is?
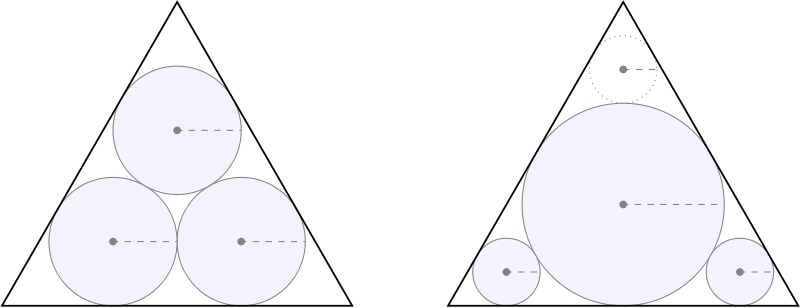
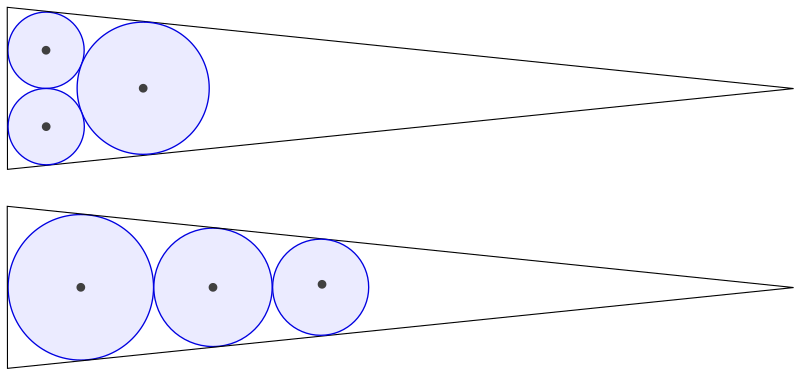
What’s the best way to squeeze three circles into a triangle so that the area of the circles is maximized? In 1803 Italian mathematician Gian Francesco Malfatti decided that the best course was to place each circle tangent to the other two and to two sides of the triangle (left) — he thought that some instance of this arrangement would give the best solution.
But that’s not actually so: In an equilateral triangle, Malfatti’s circles occupy less area than the solution on the right, found by Lob and Richmond in 1930 — their suggestion is to inscribe the largest possible circle in the triangle, then fit the second circle into one of the triangle’s three corners, and then fit the third circle into one of the five spaces now available, taking the largest available option in each case.
In the case of an equilateral triangle, Lob and Richmond’s solution is only about 1% larger than Malfatti’s. But in 1946 Howard Eves pointed out that for a long, narrow isosceles triangle (below), simply stacking three circles can cover nearly twice the area of the Malfatti circles.
Subsequent studies have borne this out — it turns out that Malfatti’s plan is never best. We now know that Lob and Richmond’s procedure will always find three area-maximizing circles — but whether their approach will work for more than three circles is an open question.
(Thanks, Larry.)
Inscriptions found in 17th-century English wedding rings, from William Jones’ Finger-Ring Lore, 1898:
A diamond ring bore the inscription “This sparke will grow.”